In what ways can capitalistic and socialistic economies converge? This question has captivated economists and policymakers for decades, as the world’s economies have evolved and intertwined. In this article, we will explore the common economic goals, market mechanisms, government interventions, hybrid models, historical examples, and future trends that shape the convergence of these two distinct economic systems.
Capitalistic and socialistic economies, despite their ideological differences, share a fundamental goal: to allocate resources efficiently to meet consumer needs. They prioritize economic growth, stability, and equity, albeit through different means.
Common Economic Goals: In What Ways Can Capitalistic And Socialistic Economies Converge
Both capitalistic and socialistic economies share common economic goals, such as:
- Efficient resource allocation:Meeting consumer needs while minimizing waste and maximizing productivity.
- Economic growth:Increasing the overall size of the economy through production and innovation.
- Stability:Maintaining low inflation, stable prices, and a predictable business environment.
- Equity:Ensuring a fair distribution of wealth and economic opportunities.
Convergence through Market Mechanisms
Market competition and price signals can drive convergence between capitalistic and socialistic economies:
- Private property:In both systems, individuals and businesses own and control assets, incentivizing efficient use.
- Profit motive:In capitalism, businesses seek profits, driving innovation and efficiency. In socialism, enterprises aim to maximize social welfare, also incentivizing productivity.
- Price signals:Prices reflect supply and demand, guiding resource allocation in both economies.
Convergence through Government Intervention
Government policies can influence the convergence of capitalistic and socialistic economies:
- Taxation:Progressive taxation in socialist economies redistributes wealth, while flat taxation in capitalist economies promotes individual incentives.
- Subsidies:Governments may subsidize certain industries or services in both systems to promote social welfare or economic growth.
- Regulations:Government regulations can protect consumers, promote competition, and ensure economic stability in both capitalist and socialist economies.
Hybrid Economic Models
Hybrid economic models combine elements of capitalism and socialism:
- Mixed economies:Allow for private ownership and market forces, while also incorporating government intervention and social welfare programs.
- Welfare states:Capitalist economies with extensive social welfare systems to provide healthcare, education, and other public services.
- Cooperative enterprises:Employee-owned businesses that combine socialist principles of worker control with capitalist principles of profit-making.
Historical Examples of Convergence
Examples of convergence between capitalistic and socialistic economies include:
- China:Has adopted a hybrid economy, combining market reforms with socialist principles.
- Scandinavian countries:Implement social welfare systems within capitalist economies, achieving high levels of economic equality and social well-being.
- Post-war Europe:Governments adopted Keynesian economic policies, blending socialist principles of government intervention with capitalist principles of private enterprise.
Future Trends and Challenges
Potential future trends that may drive convergence include:
- Technological advancements:Automation and AI may blur the lines between capital and labor, leading to new forms of economic organization.
- Climate change:Government intervention may become necessary to address environmental challenges and promote sustainable economic growth.
- Globalization:Increasing interconnectedness may foster convergence as economies adopt best practices from different systems.
Questions and Answers
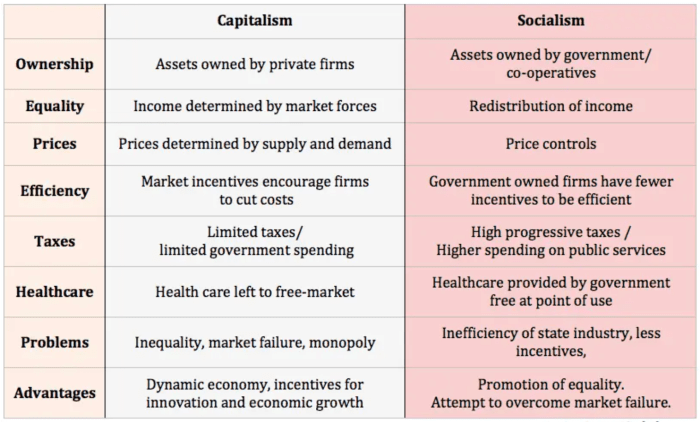
What are the key differences between capitalism and socialism?
Capitalism is characterized by private ownership of capital and means of production, while socialism emphasizes public or collective ownership and control.
How can market competition drive convergence between capitalistic and socialistic economies?
Market competition creates incentives for businesses to innovate and become more efficient, regardless of their ownership structure.